CHENOPODIUM
Chenopodium
L., Sp. Pl. ed. 1: 219. 1753; Gen. Pl. 5: 103. 1754; Boiss., Fl. Or. 4: 900; 1879; Hook. f., Fl. Brit. India 5: 5. 1890; Collett, Fl. Siml. ed. 2: 416. 1921 (Reprint 1983); Fl. China @ eFloras.org 5: 378; Clemants & Mosyakin, Fl. North Amer. @ eFloras.org 4: 267-268; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org Pakistan V. 204.
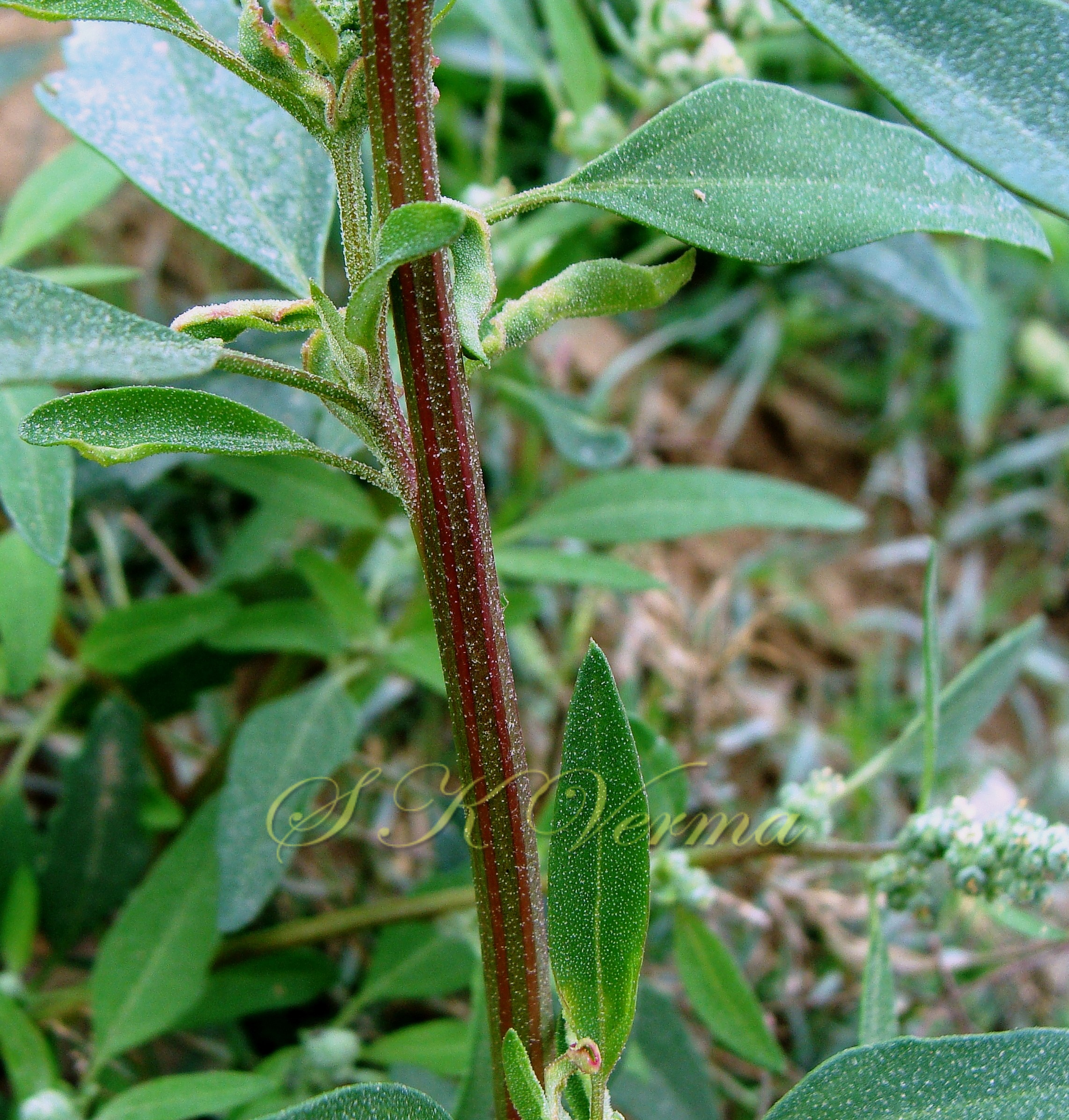
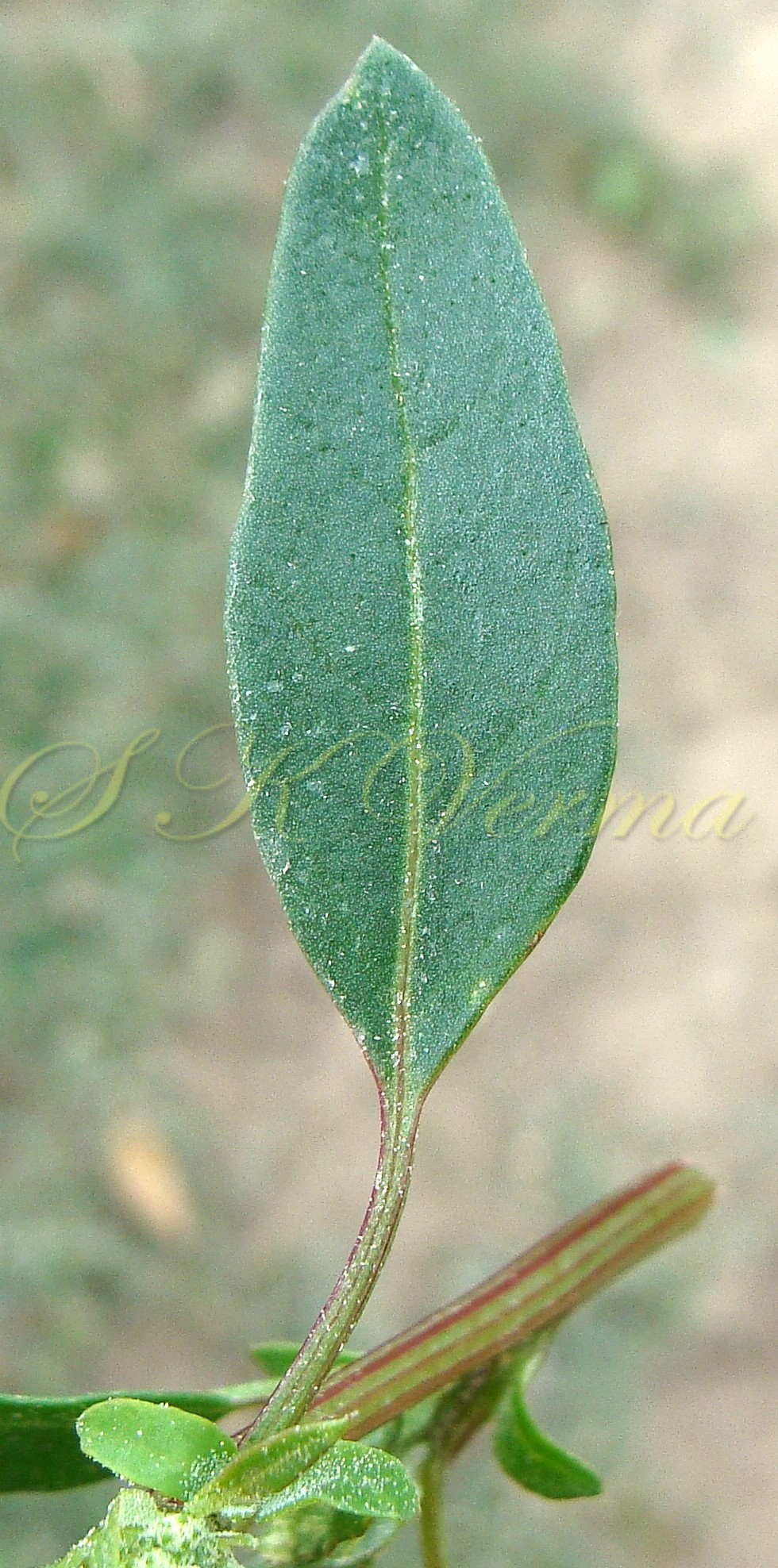
Annual or perennial herbs, young parts farinose (mealy, powdery) with vesicular hairs which later disappear or plants glandular-hairy or glabrous. Stem erect, ascending or prostrate, branched, angled, grooved. Leaves alternate, petiolate or sessile; leaf blade simple to pinnatifid, variously dentate, irregularly serrate, lobed or entire, flat, soft and narrower. Inflorescence usually a variable panicle or spiciform, formed of clusters of cymosely arranged flowers (glomerules). Flowers small, green, actinomorphic, bisexual, hypogynous, less oftenly dimorphic: terminal flowers male or bisexual and lateral flowers male. Bracteoles absent. Tepals 3-5, equal, usually connate at base, sometimes to middle or beyond, not imbricate, rounded or keeled abaxially. Stamens 5 or fewer, usually free, sometimes basally united, opposite to tepals, anthers bithecous. Ovary superior, globose, slightly depressed, rarely ovoid, unilocular with 1 ovule; style 1, short or absent; stigmas 2(-5), filiform. Fruit utricle, often enclosed in infolded perianth, indehiscent or irregularly dehiscent, pericarp membranous or slightly fleshy, adnate to seed or free. Seed horizontal or vertical, rarely oblique, lenticular or depressed globose, black, brown-black or reddish- black, lustrous.
130 species
Chenopodium album
Chenopodium album
L., Sp. Pl. ed.1: 219. 1753; Boiss., Fl. Or. 4: 901; 1879; Hook. f., Fl. Brit. India 5: 5. 1890; Collett, Fl. Siml. ed. 2: 416. 1921 (Reprint 1983); Dhaliwal & Sharma, Fl. Kullu Dist. 548. 1999; Kaur & Sharma, Fl. Sirmaur 544. 2004; Singh & Sharma, Fl. Chamba Dist. 598. 2006; Fl. China @ eFloras.org 5: 383; Fl. North Amer. @ eFloras.org 4: 296; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org Pakistan V. 204.
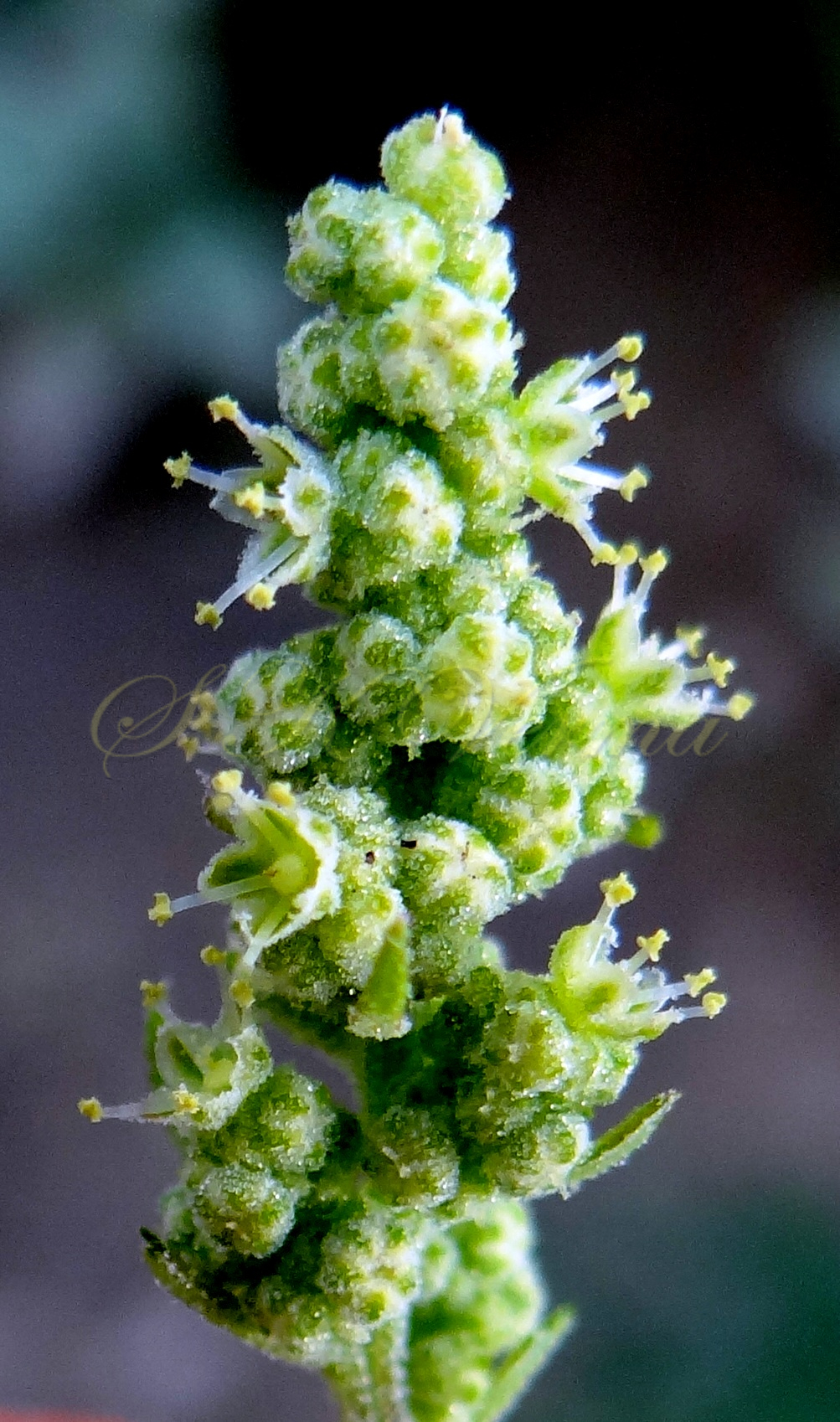
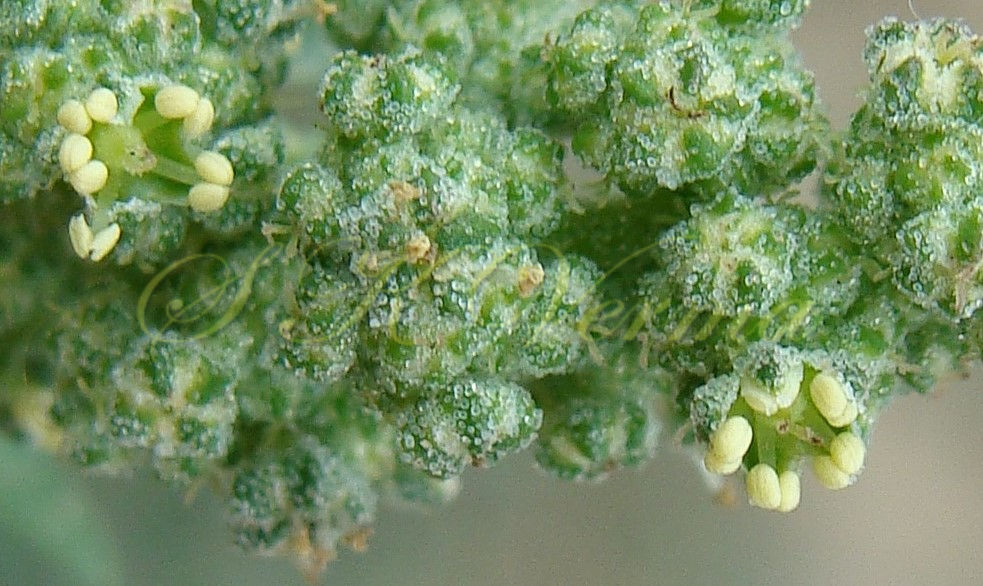
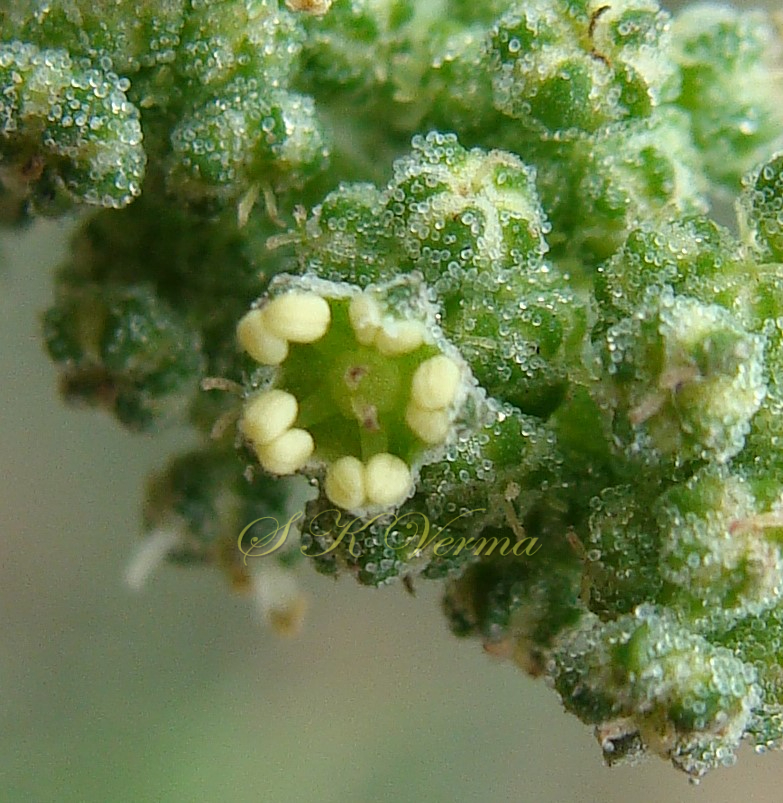
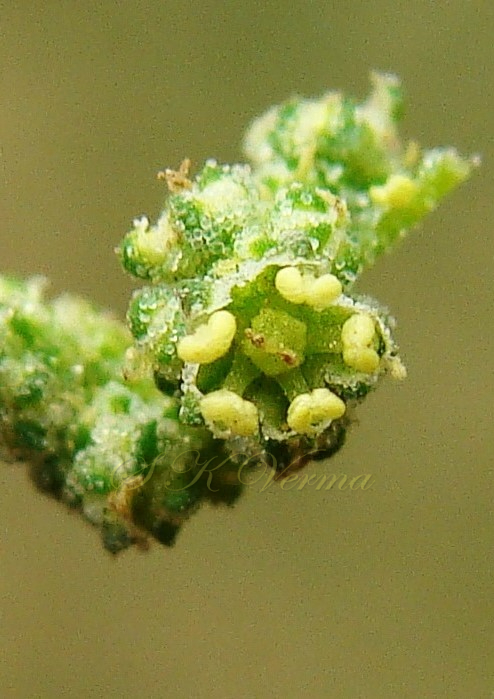
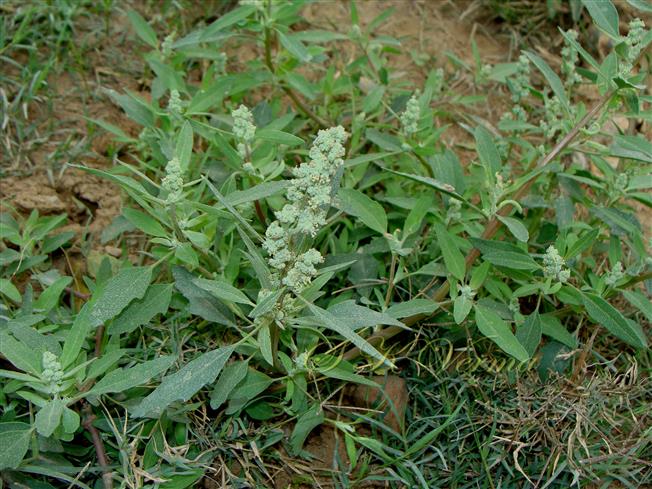
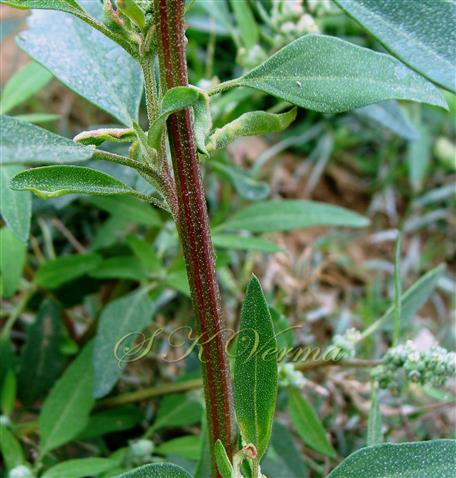
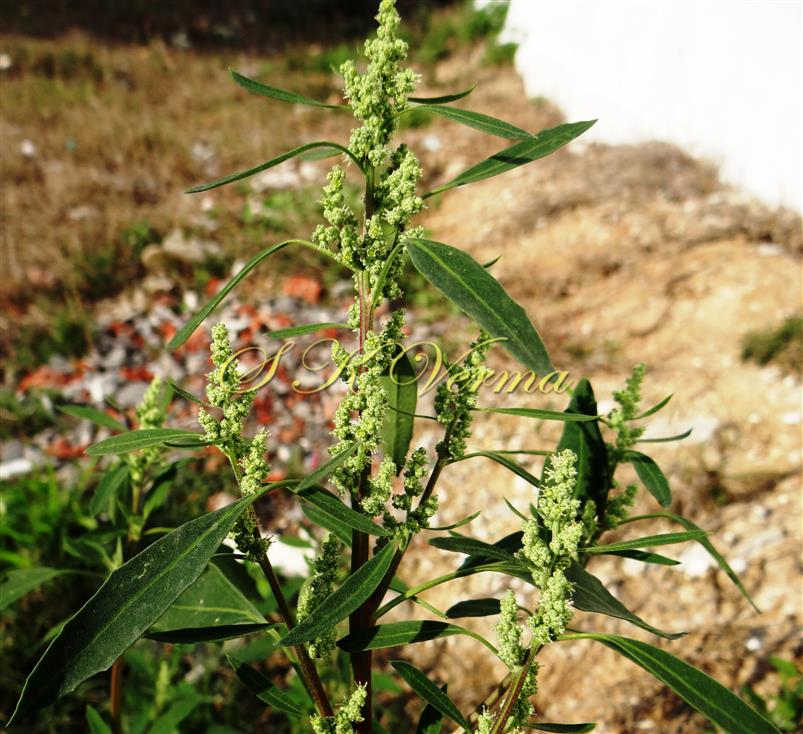
Annual herb, up to 2.5 m tall, often farinose (mealy) with vesicular hairs, especially the young stem, flowers and abaxial surface of leaves. Stem erect or ascending, simple or branched, angular-ribbed, often red or green, striated, glabrous. Leaves alternate; petiole nearly equal to or shorter than leaf blade, white mealy when young, finally becoming glabrous; leaf blade 0.5-10 cm x 0.3-7 cm, shape extremely variable: lower and medium leaves rhombic-ovate or lanceolate, longer than broad, base narrowly or broadly cuneate, apex subobtuse or acute, margin irregularly serrate- dentate to entire, teeth unequal and mostly acute; uppermost leaves lanceolate, usually entire. Inflorescence usually a variable axillary or terminal, leafy or non-leafy, dense or lax panicle or spiciform, formed of clusters of cymosely arranged flowers (glomerules). Flowers minute, whitish-green, actinomorphic, bisexual, hypogynous. Tepals 5, equal, connate at base; lobes 1-1.4 mm x ca. 1 mm, not imbricate, broadly ovate to elliptic, green, keeled abaxially and longitudinally, margin white membranous, apex acute or slightly emarginate, farinose. Stamens 5, free, opposite the tepals; anthers slightly exserted, bithecous, dehiscence longitudinal. Ovary superior, globose, unilocular with 1 ovule; style short; stigmas 2, filiform, ca. 0.2 mm long. Fruit utricle, depressed ovoid, enclosed in perianth, perianth falling with fruit, pericarp thin, membranous, adnate to seed. Seed horizontal, lenticular, 1-1.5 mm in diameter, somewhat ovate, sublustrous.
Common Names: Fat hen, Lamb’s quarters, White goosefoot; Bathua (Hindi), Lunak, Baathu (Punjabi)




 with vesicular hairs-DSC02368.jpg)
 with vesicular hairs- DSC03149.jpg)








 with vesicular hairs-DSC02368.jpg)
 with vesicular hairs- DSC03149.jpg)



